Only a few years ago very few people would have heard of coeliac disease but things are different today. Most people have heard of it and many people have it or suspect that they have it. In my clinical practice of hospital gastro-enterology it used to be very rare but now barely a week goes by without me seeing a newly diagnosed patient.
But we must always be cautious about epidemics. Is it a true epidemic, that is a real increase in the frequency of a disease resulting from natural or environmental factors? Influenza epidemics for example are obvious, but not epidemics of diseases that are not generally considered to be of a non-microbial cause.
An epidemic can be spurious, false, being a reflection of medical definition and the result of deliberations by a committee. There is supposed to be a present epidemic of diabetes, but is this might be just a result of case-finding in people who consider themselves to be normal. But in addition the definition of diabetes is changing so as to include more people, a greater proportion of the population.
The definition of a disease can change, and so can the behaviour of doctors to diagnose it. It is only when a disease is fatal that the diagnosis is usually clear, but even then terminology can change. There has been a clear epidemic of coronary heart disease during the 20th century and international death statistics have defined it. When the epidemic developed there was a great increase in the total number of heart deaths, this excluding just a change in terminology.
We must be aware of these factors when we contemplate whether there is a true epidemic of coeliac disease.
 |
| Samuel Gee |
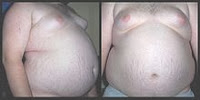
It was first recognised in children. The clinical picture was that of looseness of the bowel with fatty stools and either weight loss or failure to gain weight. The “pot belly” appearance of the children gave the name coeliac disease. It was first described by the English physician Samuel Gee, but its cause was completely unknown.
Identification of the cause
The clue to the cause was a result of the famine in the Netherlands during the Second World War. Whereas the health of the general population deteriorated with tragic results, that of children known to have coeliac disease surprisingly improved. Towards the end of the war the Netherlands was liberated and its food production was restored to its population. The famine was relieved but the children with coeliac disease became ill once again.
The cause of coeliac disease clearly lay in the diet but what it was remained far from clear. By using a nutritious food that was not in the European diet, empirical experimentation led to a diet of bananas being being identified as effective in restoring good health for these children. They became known as “banana babies”, a term now almost beyond memory.
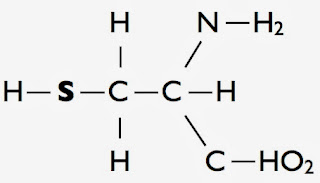
Re-introduction of a variety of normal European foods led to the recognition of wheat as the cause, and a wheat-free diet became the treatment. Further investigation identified the true culprit to be gluten, a protein component of wheat flour, and now known to be present in other cereal flours. There is however no gluten in rice flour and people with coeliac disease can eat rice without ill-effect.
It is gluten that makes dough sticky, and so rice flour with no gluten is not sticky. The bread made from rice flour (and this is what gluten-free flour actually is, combined with potato flour) is very crumbly and in this respect it is not very pleasant. There is a way around this. A small amount of egg-white can be added to gluten-free rice flour to act as a binding agent, as in other forms of cookery.
The increased awareness of coeliac disease has brought about a widespread availability of gluten-free flour and prepared foods.
The Chinese would not have had coeliac disease as their diet was based on rice and they did not have wheat. When Marco Polo visited China he was introduced to noodles, which were and still are made from rice flour with egg-white as a binding agent. Egg noodles are available in our shops and supermarkets today. On his return to Venice, Marco Polo introduced the idea of noodles to Italy, and it was later realised that wheat flour could be used without the need for egg due to the presence of gluten. Lasagne sheets had been used in Italy for the preservation of wheat during the winter, but spaghetti and other forms of pasta became a new way to preserve and a way to eat wheat. Although pasta is excluded from a coeliac disease diet, egg noodles are perfectly acceptable.
The pathology, the nature of the disease
It was in the 1960s that the pathology of coeliac disease became established. The disease process was in the jejunum, the upper part of the small intestine. The jejunum has the function of the absorption of food, a remarkably rapid process, and damage in coeliac disease leads to impairment of absorption - malabsorption. The result is a failure of absorption of essential nutriments, fats in particular.
An alternative and more accurate name for coeliac disease is Gluten Enteropathy, implying that there is intestinal disease caused by gluten.
 |
| Normal jejunal mucosa, tall villi and short crypts |
The surface of the normal jejunum is covered with finger-like villi, and this arrangement increases many-fold the surface area available for the absorption of nutrients. In coeliac disease gluten causes damage that results in the villi becoming shorter (partial villous atrophy) or absent (total villous atrophy). These changes can be seen on microscopy.
However the term “atrophy” (= wasting) is not really appropriate. Each of the villi (singular villus, adjective villous) has an associated crypt (a “pit”). The change in coeliac disease is that as the villi become shorter (partial villous atrophy) the crypts become deeper. When in more severe coeliac disease the villi flattened it is called total villous atrophy flattened. The crypts are then very deep. In other words coeliac disease is more of a hypertrophy than an atrophy. The villi have a surface of single cells which have the absorptive function. These cells are formed in the crypts and then travel up the villi and fall off the top. This journey normally takes three days but in coeliac disease it can take only twelve hours. This is indeed hypertrophy of the mucosa, excess growth, or more strictly hyperplasia, an increase in cell turnover.
The process of diagnosis
Identification of pathology relies on biopsy specimens and this was the challenge, to biopsy the lining of the jejunum without the need for potentially dangerous invasive surgery.
 |
| Crosby capsule |
The answer lay in the Crosby capsule. This was an ingenious device about the size of a 500mg medical capsule. It was swallowed and on the end of a fine tube it slowly passed though the stomach and into the jejunum, identified on X-ray. When correctly positioned it was fired by negative pressure from a syringe and then withdrawn, containing a small biopsy specimen.
 |
| Crosby capsule located in jejunum |
Jejunal biopsy using a Crosby capsule was a tedious process taking a full morning and not always being successful. I remember it well from when I was in early years of training. But it meant that very few biopsies could be undertaken, and only in patients in whom there was a very strong suspicion of the diagnosis.
Things changed in the late 1970s with the wide-spread use of gastroscopy. Most people will be aware of this, a method of examining the stomach and duodenum with a fibre-optic scope. it also allows biopsies to be taken, and this includes duodenal biopsies (from as far into the duodenum as possible) for the purpose of diagnosing coeliac disease. Although the process would take only about ten minutes, it was still minimally invasive and uncomfortable to the patient. However it enabled a much greater number of such biopsies than was possible using Crosby capsule biopsy, and therefore a greater number of people with coeliac disease were able to be diagnosed.
But then at about the year 2000 came a non-invasive test, a simple blood test, the immunological detection of antibodies. This is now used very frequently, particularly by family doctors and there is no restriction on testing. It is just a matter of the doctor or nurse ticking the box on the blood sample request form. It is usual to follow a positive blood test with a biopsy and there is a strong correlation between the two.
It has enabled a vast increase in the number of people to be tested for coeliac disease and the number of positive tests has been far greater than expected. The coeliac disease blood test is now performed with little discrimination and on people with, traditional standards, no realistic probability of coeliac disease, for example in people with just recent diarrhea.
Is a biopsy always necessary?
In practice the diagnosis of coeliac disease is based on any three of four criteria:
- a good clinical story
- positive blood test
- abnormal biopsy
- good response to a gluten free diet.
We will see that a good clinical story is not always present. The blood test can be bypassed if a biopsy is performed.
Many people are very reluctant to have a biopsy, the gastroscopy being rather unpleasant. If the patient has symptoms and a positive blood test, then a good response to a gluten free diet will clinch the diagnosis. It is when there is uncertainty that a biopsy is essential. The uncertainties can be a vague story, an equivocal blood test, and uncertainty about response to diet.
There will be further short posts on the subject of coeliac disease.